
In this style, high concern is paid both to people and production.

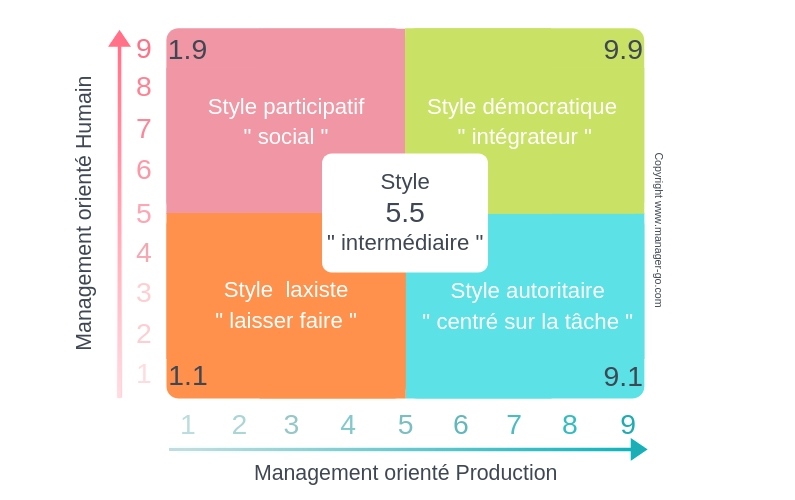
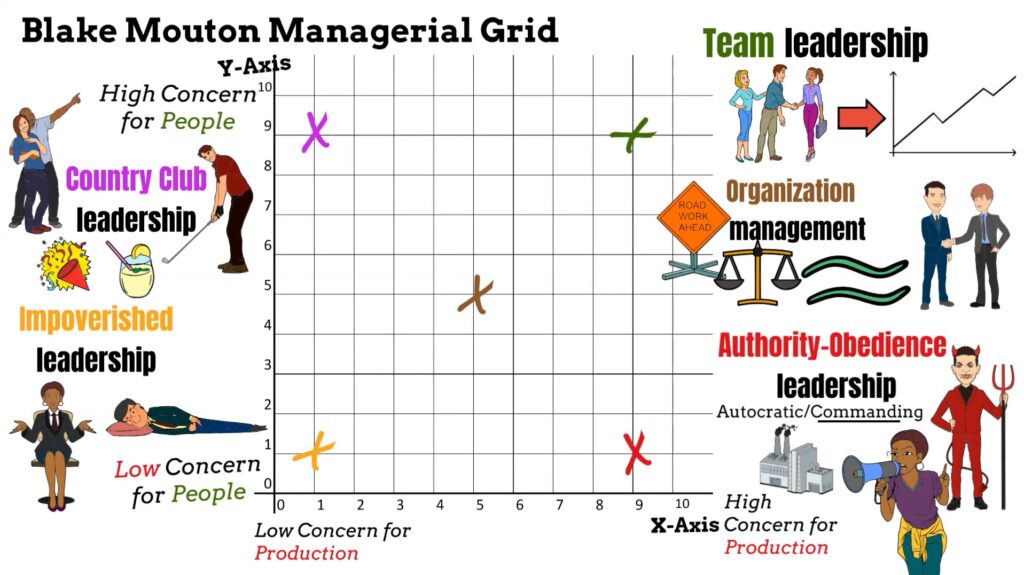
The sound (previously, team) style (9,9): contribute and commit.By giving some concern to both people and production, managers who use this style hope to achieve suitable performance but doing so gives away a bit of each concern so that neither production nor people needs are met. Managers using this style try to balance between company goals and workers' needs. The status quo (previously, middle-of-the-road) style (5,5): balance and compromise.This style is often used in cases of crisis management. This dictatorial style is based on Theory X of Douglas McGregor, and is commonly applied by companies on the edge of real or perceived failure. Managers using this style also pressure their employees through rules and punishments to achieve the company goals.
 The dictatorial (previously, produce or perish) style (9,1): in return. The resulting atmosphere is usually friendly, but not necessarily very productive. Managers using this style pay much attention to the security and comfort of the employees, in hopes that this will increase performance. This style has a high concern for people and a low concern for production. The accommodating (previously, country club) style (1,9): yield and comply. The main concern for the manager is not to be held responsible for any mistakes, which results in less innovation decisions. Managers use this style to preserve job and job seniority, protecting themselves by avoiding getting into trouble. In this style, managers have low concern for both people and production. The indifferent (previously called impoverished) style (1,1): evade and elude. The resulting leadership styles are as follows: The model is represented as a grid with concern for production as the x-axis and concern for people as the y-axis each axis ranges from 1 (Low) to 9 (High). In 1999, the grid managerial seminar began using a new text, The Power to Change. The theory was updated with two additional leadership styles and with a new element, resilience. The grid theory has continued to evolve and develop. The optimal leadership style in this model is based on Theory Y. This model originally identified five different leadership styles based on the concern for people and the concern for production. The managerial grid model or managerial grid theory (1964) is a style leadership model developed by Robert R.
The dictatorial (previously, produce or perish) style (9,1): in return. The resulting atmosphere is usually friendly, but not necessarily very productive. Managers using this style pay much attention to the security and comfort of the employees, in hopes that this will increase performance. This style has a high concern for people and a low concern for production. The accommodating (previously, country club) style (1,9): yield and comply. The main concern for the manager is not to be held responsible for any mistakes, which results in less innovation decisions. Managers use this style to preserve job and job seniority, protecting themselves by avoiding getting into trouble. In this style, managers have low concern for both people and production. The indifferent (previously called impoverished) style (1,1): evade and elude. The resulting leadership styles are as follows: The model is represented as a grid with concern for production as the x-axis and concern for people as the y-axis each axis ranges from 1 (Low) to 9 (High). In 1999, the grid managerial seminar began using a new text, The Power to Change. The theory was updated with two additional leadership styles and with a new element, resilience. The grid theory has continued to evolve and develop. The optimal leadership style in this model is based on Theory Y. This model originally identified five different leadership styles based on the concern for people and the concern for production. The managerial grid model or managerial grid theory (1964) is a style leadership model developed by Robert R.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
